Taxonomy or Classification of meditation techniques
Are all meditation techniques the same?
Different practices often produce different results
As doctors increasingly prescribe meditation to patients for stress-related disorders, scientists are gaining a better understanding of how different techniques from Buddhist, Chinese, and Vedic traditions produce different results.
A new paper published in Consciousness and Cognition discusses three categories to organize and better understand meditation:
- Focused attention—concentrating on an object or emotion;
- Open monitoring—being mindful of one's breath or thoughts;
- Automatic self-transcending—meditations that transcend their own activity—a new category introduced by the authors.
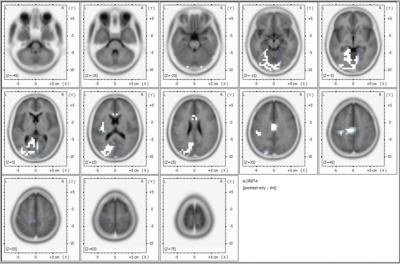
Each category was assigned EEG bands, based on reported brain patterns during mental tasks, and meditations were categorized based on their reported EEG.
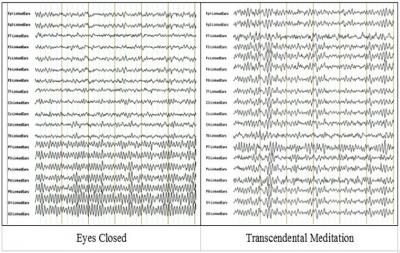
"The idea is that meditation is, in a sense, a 'cognitive task,' and EEG frequencies are known for different tasks," said Fred Travis, Ph.D., co-author, and Director of the Center for Brain, Consciousness, and Cognition at Maharishi University of Management.
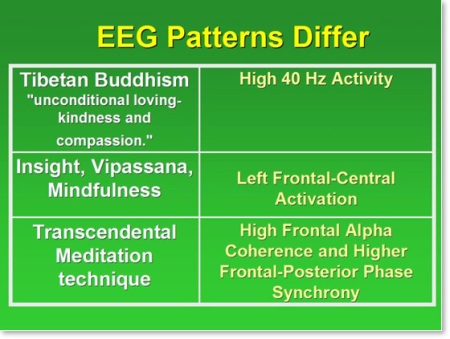
- Focused attention, characterized by beta/gamma activity, included meditations from Tibetan Buddhist (loving kindness and compassion), Buddhist (Zen and Diamond Way), and Chinese (Qigong) traditions.
- Open monitoring, characterized by theta activity, included meditations from Buddhist (Mindfulness, and ZaZen), Chinese (Qigong), and Vedic (Sahaja Yoga) traditions.
- Automatic self-transcending, characterized by alpha1 activity, included meditations from Vedic (Transcendental Meditation) and Chinese (Qigong) traditions.
Between categories, the included meditations differed in focus, subject/object relation, and procedures. These findings shed light on the common mistake of averaging meditations together to determine mechanisms or clinical effects.
"Meditations differ in both their ingredients and their effects, just as medicines do. Lumping them all together as "essentially the same" is simply a mistake," said Jonathan Shear, Ph.D., co-author, professor of philosophy at Virginia Commonwealth University in Richmond, and the author of several books and publications on meditation.
"Explicit differences between meditation techniques need to be respected when researching physiological patterns or clinical outcomes of meditation practices," said Dr. Travis. "If they are averaged together, then the resulting phenomenological, physiological, and clinical profiles cannot be meaningfully interpreted."

Meditations differ in both their ingredients and their effects, just as medicines do. Lumping them all together as "essentially the same" is simply a mistake
Review - Focused attention, open monitoring and automatic self-transcending : Categories to organize meditations from Vedic, Buddhist and Chinese traditions
Abstract : This paper proposes a third meditation-category — automatic self-transcending — to extend the dichotomy of focused attention and open monitoring proposed by Lutz.
Automatic selftranscending includes techniques designed to transcend their own activity. This contrasts with focused attention, which keeps attention focused on an object; and open monitoring, which keeps attention involved in the monitoring process.
Each category was assigned EEG bands, based on reported brain patterns during mental tasks, and meditations were categorized based on their reported EEG.
Focused attention, characterized by beta/gamma activity, included meditations from Tibetan Buddhist, Buddhist, and Chinese traditions. Open monitoring, characterized by theta activity, included meditations from Buddhist, Chinese, and Vedic traditions. Automatic self-transcending, haracterized by alpha1 activity, included meditations from Vedic and Chinese traditions.
Between categories, the included meditations differed in focus, subject/object relation, and procedures. These findings shed light on the common mistake of averaging meditations together to determine mechanisms or clinical effects.
journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/concog